
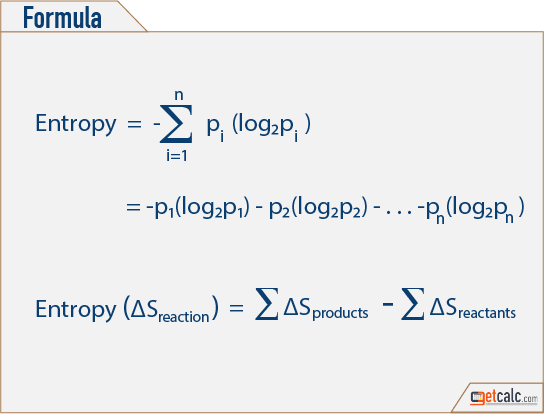
This can result in an increase or decrease in the system’s randomness, and thus in an increase or decrease in entropy. The changes in entropy in chemical reactions are caused by the rearranging of atoms and molecules, which alters the system’s initial order. Entropy is higher in a system with a high degree of disorderliness.Įntropy is a state function factor, which means that its value is independent of the thermodynamic process’s pathway and is solely a determinant of the system’s beginning and final states. Entropy ChangeĮntropy Change can be described as a shift in a thermodynamic system’s state of disorder caused by the conversion of heat or enthalpy into work. It is for this reason that the Entropy Change is calculated. This is measured by entropy, a metric.Įntropy cannot be described in a single point and must be measured as a change because the rule of thermodynamics states that energy cannot be created or destroyed but may be changed from one form to another. It is virtually impossible to devote all of one’s energy to work because energy is what allows one to perform labor. To put it another way, entropy shows us how much energy does not convert into labor and instead contributes to the disorder of the system. It aids in the reinterpretation of thermodynamics’ second law.Įntropy is proportional to the degree of disorder in a thermodynamic process the higher the degree of disorder, the higher the entropy. Entropy is an intriguing concept because it casts doubt on the idea of complete heat transfer. The term disorder refers to the irregularity or lack of uniformity in a thermodynamic system.īecause the value of entropy or Entropy Change depends on the substance present in a thermodynamic system, the letter ‘S’ is used to represent it.

Randomness could apply to the entire world, a single chemical reaction, or even heat transport and exchange. Copper Sulfate Formula - Structure, Properties, Uses, Sample QuestionsĮntropy is a measure of disorder or unpredictability.How to calculate the Molarity of a Solution?.Aluminium Chloride Formula - Structure, Properties, Uses, Sample Questions.Silicon Dioxide Formula - Structure, Properties, Uses, Sample Questions.Borax Formula - Structure, Properties, Uses, Sample Questions.Lead Iodide Formula - Structure, Properties, Uses, Sample Questions.

Chloroform Formula - Structure, Properties, Uses, Sample Questions.Glycerol Formula - Structure, Properties, Uses, Sample Questions.Sodium Nitrate Formula - Structure, Properties, Uses, Sample Questions.Propan-2-Ol Formula - Structure, Properties, Uses, Sample Questions.Dimethylglyoxime Formula - Structure, Properties, Uses, Sample Questions.Formaldehyde Formula - Structure, Properties, Uses, Sample Questions.Acetone Formula - Structure, Properties, Uses, Sample Questions.Lactic Acid Formula - Structure, Properties, Uses, Sample Questions.Potassium Hydroxide Formula - Structure, Properties, Uses, Sample Questions.Normality - Definition, Formula, Equations and Solved Examples.Citric Acid Formula - Structure, Properties, Uses, Sample Questions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
